ASTM A182 F316 Flange has excellent forming and welding characteristics. It is readily brake or roll formed into a variety of parts for applications in the industrial fields. Grade 316 also has outstanding welding characteristics. Post-weld annealing is not required when welding thin sections.
ASTM A182 F316 Flange Material
ASTM A182 F316 Flanges are very common in usage due to their improved corrosion resistance properties. A182 F316 Material has an addition of molybdenum in the composition which brings about the extra corrosion resistance. 316 Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges are made up of austenitic stainless steel with chromium and nickel as alloy material. Therefore Stainless Steel 316 Weld Neck Flanges are stronger and durable. For extended usage and for welding and strength, the A182 F316 Material is used.
ASTM A182 F316 Flange Chemical Composition
| CHEMICAL | LIMITS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | N |
| ASTM A182 F316 | MIN | 10.0 | 16.0 | 2.00 | ||||||
| MAX | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 14.0 | 18.0 | 3.00 | 0.01 |
Chromium plays a key role in stainless steel.it can improving the corrosion resistance of the material. In ASTM A182 F316 flanges, this high chromium content enables it to resist a variety of corrosive environments.
Stainless Steel 316 Flange Mechanical Property
| MATERIAL | T.S (MPA) | Y.S (MPA) | EL % | R/A % |
| ASTM A182 F316 | 515 min | 205 min | 30 min | 50 min |
The yield strength of A182 F316 flange is generally not less than 205MPa. The yield strength is the stress value when the material begins to produce obvious plastic deformation. In the pipeline system, the flange needs to withstand a certain amount of pressure and tension. The yield strength ensures that the flange will not undergo excessive plastic deformation. The yield strength can ensure the stability of the pipeline connection.
ASTM A182 F316 Flange Dimension
ASTM A182 F316 flanges include threaded flanges, socket weld flanges, threaded flanges, blind flanges, lap joint flanges, weld neck flanges. The pressure ratings are 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500#. The commonly used pressure is 150#.
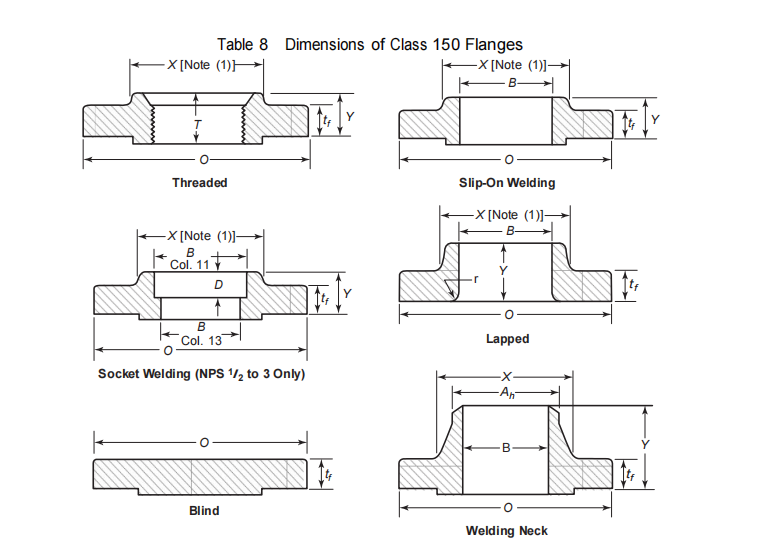
Dimensions of Class 150 Flanges (Cont’d)
| Nominal Pipe Size, NPS |
Outside Diameter of Flange, O |
Minimum Thickness of Flange, tf [Notes (2)-(4)] |
Minimum Thickness Lap Joint, tf |
Diameter of Hub, X |
Hub Diameter Beginning of Chamfer Welding Neck, Ah [Note (5)] |
Length Through Hub | Minimum Thread Length Threaded, T [Note (6)] |
Bore | Welding Neck/ Socket Welding, B [Note (7)] |
Corner Bore Radius of Lapped Flange and Pipe, r |
Depth of Socket, D |
|||
| Threaded/ Slip-on/ Socket Welding, Y |
Lapped, Y |
Welding Neck, Y |
Minimum Slip-on/ Socket Welding, B |
Minimum Lapped, B |
||||||||||
| 1/2 | 90 | 9.6 | 11.2 | 30 | 21.3 | 14 | 16 | 46 | 16 | 22.2 | 22.9 | 15.8 | 3 | 10 |
| 3/4 | 100 | 11.2 | 12.7 | 38 | 26.7 | 14 | 16 | 51 | 16 | 27.7 | 28.2 | 20.9 | 3 | 11 |
| 1 | 110 | 12.7 | 14.3 | 49 | 33.4 | 16 | 17 | 54 | 17 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 26.6 | 3 | 13 |
| 1 1/4 | 115 | 14.3 | 15.9 | 59 | 42.2 | 19 | 21 | 56 | 21 | 43.2 | 43.7 | 35.1 | 5 | 14 |
| 1 1/2 | 125 | 15.9 | 17.5 | 65 | 48.3 | 21 | 22 | 60 | 22 | 49.5 | 50.0 | 40.9 | 6 | 16 |
| 2 | 150 | 17.5 | 19.1 | 78 | 60.3 | 24 | 25 | 62 | 25 | 61.9 | 62.5 | 52.5 | 8 | 17 |
| 2 1/2 | 180 | 20.7 | 22.3 | 90 | 73.0 | 27 | 29 | 68 | 29 | 74.6 | 75.4 | 62.7 | 8 | 19 |
| 3 | 190 | 22.3 | 23.9 | 108 | 88.9 | 29 | 30 | 68 | 30 | 90.7 | 91.4 | 77.9 | 10 | 21 |
| 3 1/2 | 215 | 22.3 | 23.9 | 122 | 101.6 | 30 | 32 | 70 | 32 | 103.4 | 104.1 | 90.1 | 10 | |
| 4 | 230 | 22.3 | 23.9 | 135 | 114.3 | 32 | 33 | 75 | 33 | 116.1 | 116.8 | 102.3 | 11 | |
| 5 | 255 | 22.3 | 23.9 | 164 | 141.3 | 35 | 36 | 87 | 36 | 143.8 | 144.4 | 128.2 | 11 | |
| 6 | 280 | 23.9 | 25.4 | 192 | 168.3 | 38 | 40 | 87 | 40 | 170.7 | 171.4 | 154.1 | 13 | |
| 8 | 345 | 27.0 | 28.6 | 246 | 219.1 | 43 | 44 | 100 | 44 | 221.5 | 222.2 | 202.7 | 13 | |
| 10 | 405 | 28.6 | 30.2 | 305 | 273.0 | 48 | 49 | 100 | 49 | 276.2 | 277.4 | 254.6 | 13 | |
| 12 | 485 | 30.2 | 31.8 | 365 | 323.8 | 54 | 56 | 113 | 56 | 327.0 | 328.2 | 304.8 | 13 | |
| 14 | 535 | 33.4 | 35.0 | 400 | 355.6 | 56 | 57 | 125 | 57 | 359.2 | 360.2 | Note(8) | 13 | |
| 16 | 595 | 35.0 | 36.6 | 457 | 406.4 | 62 | 64 | 125 | 64 | 410.5 | 411.2 | Note(8) | 13 | |
| 18 | 635 | 38.1 | 39.7 | 505 | 457.0 | 67 | 68 | 138 | 68 | 461.8 | 462.3 | Note(8) | 13 | |
| 20 | 700 | 41.3 | 42.9 | 559 | 508.0 | 71 | 73 | 143 | 73 | 513.1 | 514.4 | Note(8) | 13 | |
| 24 | 815 | 46.1 | 47.7 | 663 | 610.0 | 81 | 83 | 151 | 83 | 616.0 | 616.0 | Note(8) | 13 | |
316 vs 316L Stainless Steel: What’s the Difference?
316 and 316L stainless steel are both marine-grade steels, but they do possess some key differences. 316L has a lower proportion of carbon in its composition. To qualify as 316L stainless steel, the amount of carbon cannot exceed 0.03%. This decreases the risk of carbon precipitation, making it a better option for welding to ensure maximum corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel 316 Flange Advantages
316 stainless steel has very low responsiveness to magnetic fields. Unlike basic stainless steels, which are ferromagnetic, most stainless steel varieties are austenitic — or effectively nonmagnetic.
ASTM A182 F316L Flange Advantages
However, some ASTM A182 F316 flanges can undergo processes, like cold forming and welding. The austenitic crystal structure is transformed into ferromagnetic martensite. 316L steel is more susceptible to gaining some degree of magnetism.
Latest News
 02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...
02 8 月 2019Copper Nickel Flanges UNS C70600Zizi offers ISO certified copper nickel flanges, stores large quantity of Cu-Ni 90/10 weld neck flan...  29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...
29 7 月 2019Stainless Steel Buttweld Fittings ManufacturerZizi is stainless steel buttweld fittings manufacturer, we offer stainless steel pipe elbow, tee, ca...  19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
19 7 月 2019Steel Pipe Nipple Types, Dimensions and MaterialsBasic pattern of steel pipe nipple is a short piece of pipe with threads at both end or at one end....
